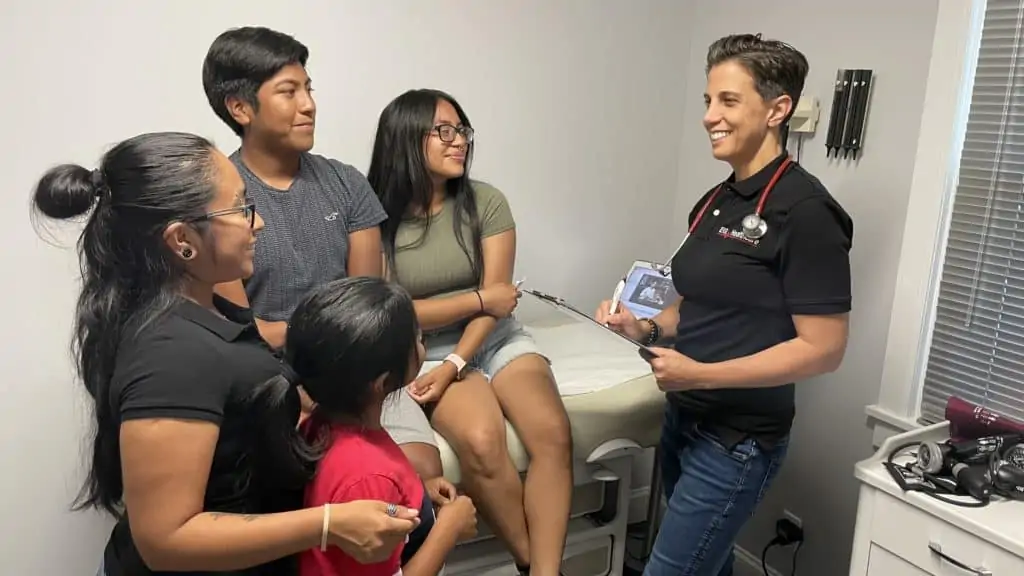
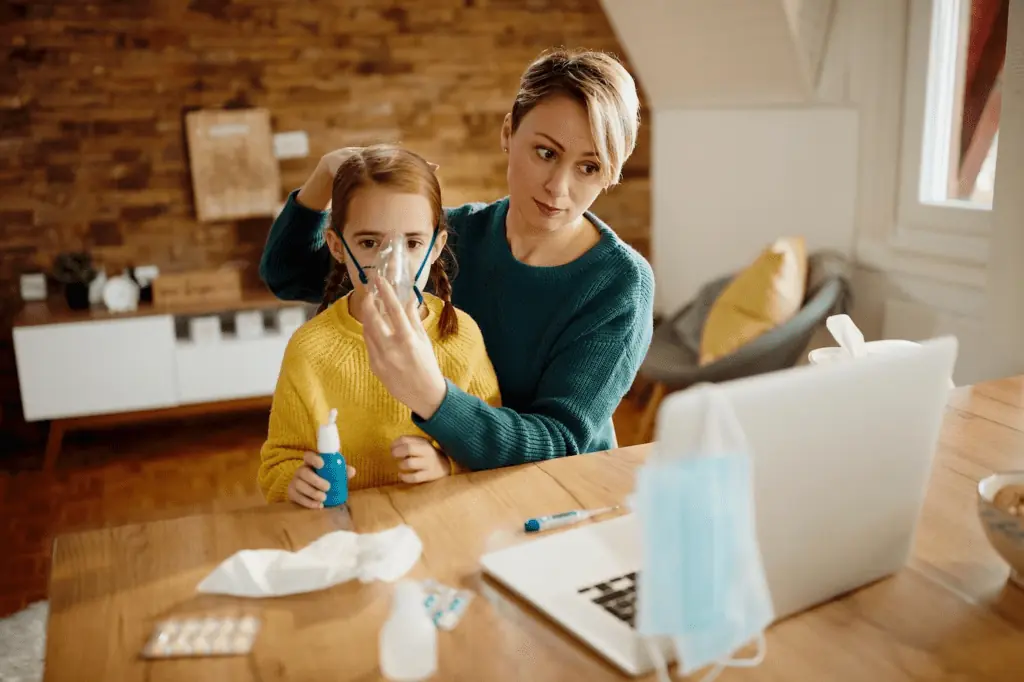
Hey there! Are you ready to dive into better health care? Well, let me explain why having a primary care provider changes everything. Imagine that you have a go-to person who is like your own personal healthcare superhero. And this person is always there to help guide and support you on your path to healing. So, let’s consider why choosing a primary care provider is the key to better health care.
Holistic Approach to Care
There’s more than meets the eye when it comes to your health. This is where a primary care provider comes in. They use a method that looks at your mind, body, and spirit. They don’t just look at the signs on the surface. Instead, they dig deep into your health and ensure no stone is left unturned.
Imagine having a healthcare partner who looks at the bigger picture. This person connects the dots between your physical health, mental well-being, and lifestyle choices. That’s what a primary care provider does. They understand your health isn’t just a series of isolated incidents—it’s a tapestry woven together by various factors.
Preventive Care and Early Detection of Risks
One superpower of primary care providers is their focus on care that helps people stay healthy. They believe that an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. Moreover, they don’t wait for problems to happen. Instead, they work with you to stop them from happening in the first place. In addition, they are like Sherlock Holmes when it comes to health care. They are always on the lookout for possible health risks and weak spots.
Routine screenings become their trusted partner in the fight against health problems that may be hiding in the background. From checking your blood pressure and cholesterol to mammograms and colonoscopies, your primary care provider ensures you stay healthy. These tests serve as early warning systems, catching red flags before they become full-blown health problems.
And when it comes to finding problems early, a primary care provider is like a guard who is always on the lookout for signs that could mean trouble is coming. They are good at finding minor signs that other people might miss. By finding problems early, they can act quickly to stop them from worsening and becoming big health problems.
Continuity of Care
Think of your primary care provider as the conductor who ensures all the other doctors and treatments work well together. They know a lot about your medical background, your current health problems, and the medicines you are getting. With this information, they can put together the different parts of your healthcare puzzle to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Minimizing Conflicting or Duplicative Care
With a primary care provider in charge, you can say goodbye to the stress of healthcare that doesn’t work together. They connect the different parts of your health care into a single plan for your health. They’re like the glue that holds your healthcare team together and makes it easier for everyone to work together.
But it’s not just about avoiding conflicting care; it’s also about reducing efforts done twice. Your primary care provider is like a spy who works hard to make sure you don’t waste time or money on tests or treatments you don’t need. They look out for you and make sure you don’t have medical procedures that aren’t required.
With continuity of care, you won’t have to repeat your medical background at every new doctor’s office, which can be annoying. Your primary care provider keeps a full health record to ensure everything gets tackled.
Personalized Health Guidance
Your primary care provider takes the time to learn about you as a person, not just as a patient. They look closely at your medical background, the choices you’ve made in your life, and your unique situation. They look for clues about your health so that they can put together the correct type of personalized care.
Armed with this information, they become your health advisor and give you specific advice on how to avoid getting sick. It’s like having a personalized plan for getting healthier. They find your risk factors, like high blood pressure, a history of heart disease in your family, or other things that could be bad for your health. Then, they work with you to make a plan of action—a unique way to keep those risks away.
Tailored Recommendations
Personalized health advice goes beyond just keeping people from getting sick. It also includes tips for living a good life and caring for yourself. They give advice on nutrition, exercise, dealing with stress, and other things that can make a big difference in your general health.
Imagine having someone who knows your goals and dreams and helps you make a plan to reach them. That’s the power of health advice that’s tailored to you. Your primary care provider gives you the tools you need to take charge of your health, make decisions based on facts, and make changes that will help you in the long run.
Long-term Monitoring and Care for Chronic Diseases
A primary care provider is important for long-term monitoring and care for people with chronic illnesses. They work closely with you to make a treatment plan unique to your health, symptoms, and goals. They provide ongoing support, ensuring that your treatment plan is optimized and adjusted as needed.
Monitoring and Collaborating with Specialists
And this is where the magic of working together comes in. Your main care provider and specialists work together to make a team that looks out for your health. They make sure that different experts can talk to each other and work together well. They put together all the pieces of your health care, working toward a complete treatment plan for every part of your illness.
Imagine having a dream team of doctors and nurses who all care about your long-term health. Your primary care provider is in charge and works with specialists. This ensures your treatment plan is the best it can be and you get the best care possible. It’s a great mix of knowledge, experience, and a shared interest in your health.
Conclusion
Having a primary care provider by your side is like having a trusted friend who knows your story, listens to your worries, and helps you toward your best health. They become your go-to person and someone you can talk to about your health and your goals.
When you have a primary care provider, you can trust and talk to them freely. They give you a safe place to talk about your problems. You can ask questions and get clear and easy-to-understand answers. No more getting lost in a sea of medical words; your primary care provider speaks your language.
They become the main person you talk to about your health care and coordinate your care like the director of an orchestra. They make it easy for experts and treatments to work together. So, care doesn’t get mixed up or done twice. With their help, you can get care that is coordinated and effective.