
We know, we know—after all, who wants to talk about their thymus? It’s not like anyone’s ever heard of it, and it doesn’t seem like there’s much to say about it. But trust us: if you don’t take care of this little organ, it could be trouble for your whole body.
So take a look at these signs and symptoms of thymus disorders, and watch out for yourself!
What Is The Thymus?
The thymus is a small organ that sits just above the heart in the chest. It’s part of the lymphatic system, which is responsible for making new white blood cells and filtering out old ones.
The thymus is most active during childhood when it helps children develop their immune systems. When they’re older, and their immune systems are more developed, their thymuses start to shrink in size and are replaced by fat.
Functions Of The Thymus
The thymus helps the body fight off infections by producing new cells that recognize bacteria or viruses that have invaded the body. T cells are lymphocytes (white blood cells) that travel through the bloodstream looking for invaders. Then, they attack and destroy these invaders when they find them. The thymus also produces antibodies, which are proteins made by B cells that can attach to specific invaders.
The thymus is part of the lymphatic system, which consists of all the organs and tissues that produce and store white blood cells. White blood cells are part of our immune system — they help us fight off infections and other diseases. The lymphatic system also includes organs such as the spleen, tonsils, and adenoids (which are found in your neck), appendixes (found in your abdomen), Peyer’s patches (found on your small intestine), bone marrow (in bones), and lymph nodes (small structures that form part of your immune system).
Disorders That Affect The Thymus Gland
The thymus gland can be affected by several different disorders. These conditions can cause swelling (inflammation) or changes in the size or shape of your thymus gland:
DiGeorge Syndrome
A birth defect in which the thymus is either absent or severely underdeveloped. Infants born with DiGeorge syndrome are more susceptible to illness because of their severe immunodeficiency.
Thymoma And Thymic Carcinoma
Thymoma and thymic carcinoma are two types of tumors that can affect the thymus gland. Thymic carcinoma is rare cancer that occurs in people with malignant thymomas (tumors) for many years. Malignant tumors are cancers that start in the body’s tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease, which means that your body’s immune system mistakenly attacks your own healthy tissue. In this case, your body’s antibodies attack the thymus gland and cause it to become underactive.
Pure red cell aplasia
Pure red cell aplasia is usually caused by an autoimmune disease, which means that your immune system mistakenly attacks your own body’s cells and tissues. In this case, it attacks your bone marrow—where red blood cells are made—and prevents it from producing enough of them.
Hypogammaglobulinemia is a condition in which the body produces too few antibodies to fight off infections and disease. It’s most commonly seen in people who have had their spleens removed or damaged by chemotherapy or other treatments for cancer. It can also be caused by certain genetic disorders like DiGeorge syndrome.
Signs And Symptoms of Thymus Disorders
The thymus gland is an important part of your immune system. It helps to make T-cells, which help fight infections and diseases. If you have a problem with your thymus gland, it can affect the way your body works and make it harder for the body to fight off infections.
So, let’s talk about some of the signs that something might be wrong with your thymus gland.
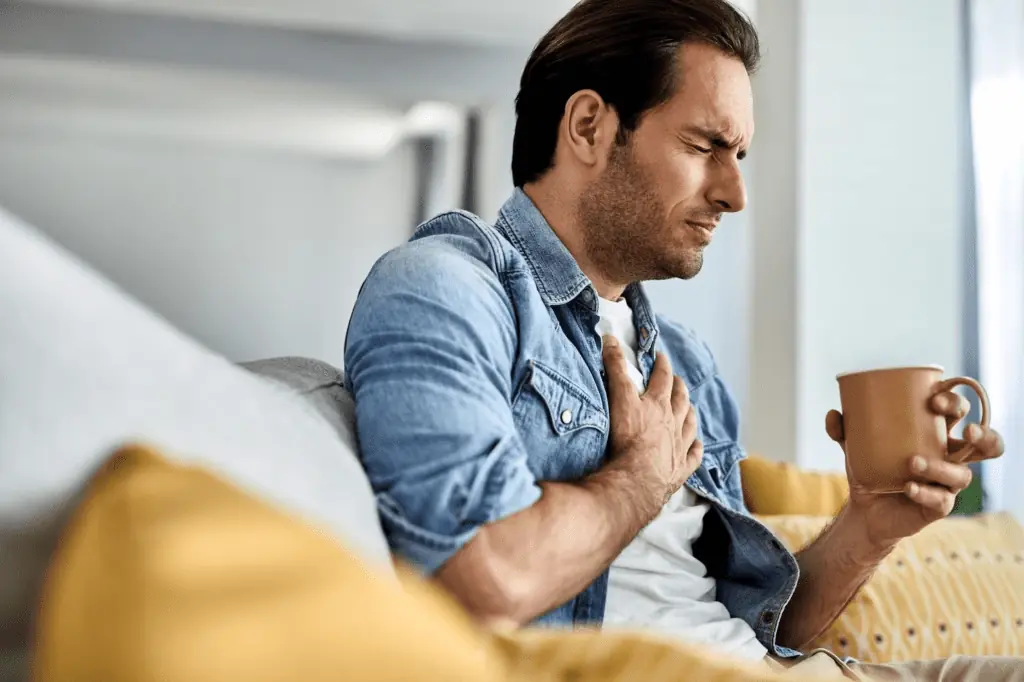
Chest Pain
Chest pain is one of the most common symptoms associated with the thymus gland. The thymus is located in your chest, so it makes sense that you might experience chest pain if there’s something wrong with it.
It’s important to know that chest pain can also be caused by other things besides an issue with your thymus gland, so it’s best to talk to your doctor if you notice this kind of symptom.
Shortness Of Breath
Shortness of breath that lasts more than a few minutes can be a warning sign that something could be wrong with your thymus gland. Remember, the thymus gland is located in the upper chest.
When you experience shortness of breath, it’s usually because your body is having trouble moving air through the lungs or getting enough oxygen into the blood. This could be caused by inflammation in the lungs, which makes it difficult for them to expand and contract.
Weight Loss
One of the first signs that something might be wrong with your thymus gland is unexplained weight loss. If you start to lose weight without trying, and can’t explain it by diet or exercise changes, then this could be a sign of thymus gland disorders.
Persistent Coughing
You may have a persistent cough if your thymus gland is malfunctioning. The problem with the thymus gland is that it produces too many white blood cells, which can cause the lung tissue to become inflamed. This inflammation can cause you to cough up thick mucus. If you are experiencing a persistent cough, it’s important for you to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Trouble Swallowing
Trouble swallowing may indicate something is wrong with your thymus gland. While this is a common symptom of many problems, it’s especially important to pay attention if you’re having trouble swallowing liquids. Your throat may feel swollen or tight, or you might notice pain when swallowing.
Hoarse Voice
A hoarse voice can signal a problem with your thymus gland. When your thymus is not functioning properly, it will stop producing white blood cells, which will, in turn, cause infections throughout your body. These infections can cause swelling in the throat or vocal cords, resulting in a hoarse voice.
Dizziness And Headache
If you’ve been feeling lightheaded or have headaches, it could be a sign that something’s not right with your thymus gland. Many people experience these symptoms when they’re feeling sick, but if you’ve noticed them more often than usual, it might mean that something is wrong with your immune system.
Swelling in your face, neck, or upper chest
If you notice swelling in this area, it could be a sign that something is wrong with your thymus gland. This includes the lymph nodes and other parts of your immune system.
The swelling might start slowly and get progressively worse over time. It’s important to see a doctor if you notice swelling in this area because it can be a symptom of something more serious.
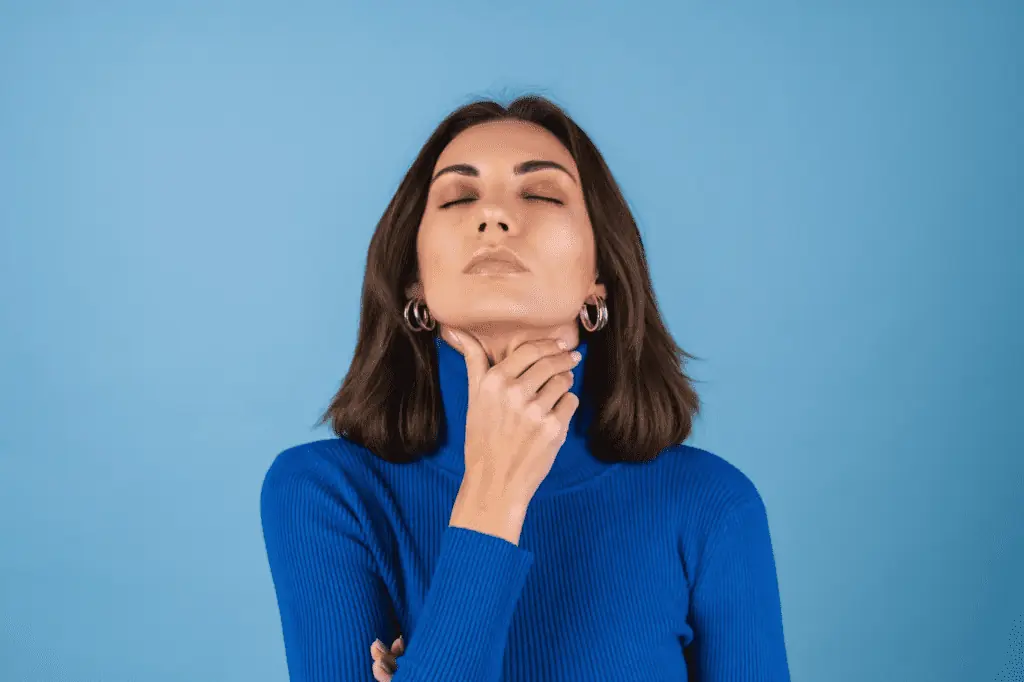

Thymus Vs. Thyroid: They’re Not The Same Thing
You might be confused by the term “thymus” and “thyroid.” While they are both important to your health, they are not the same thing.
The thymus is a gland in your chest that produces white blood cells. It also helps your body learn how to fight off infections. The thyroid gland is located in your neck and produces hormones that control metabolism, growth, and development.
Takeaways
Although its presence may have gone unnoticed, the thymus gland is essential to your health. It’s a major part of your immune system and helps your body learn how to fight off infections. The thymus also helps keep you from getting sick when you’re young, but it starts to shrink as you age.
Fortunately, by the time you reached adolescence, the majority of your T-cells had grown, and they should have helped defend you against sickness and infection for the rest of your life. Moreover, thymus-related disorders are quite rare. Check with your physician if you have thymus discomfort or other symptoms of thymus disorders.